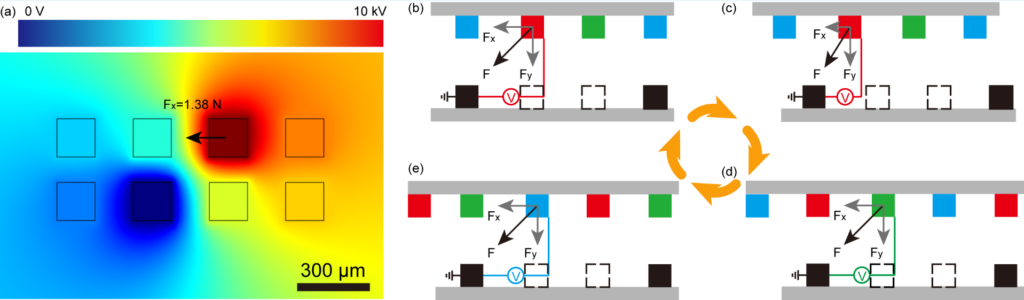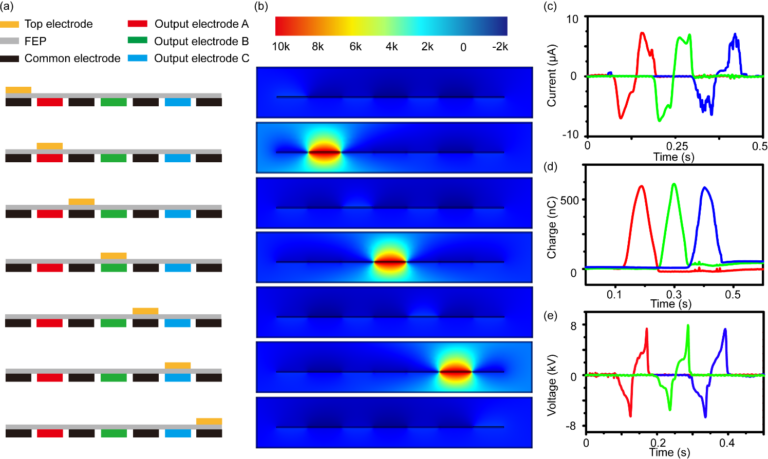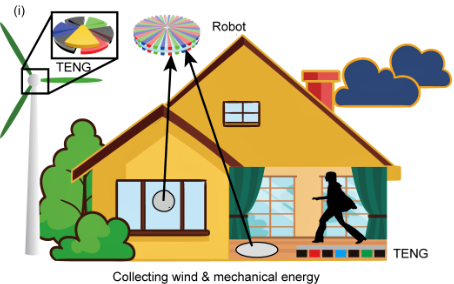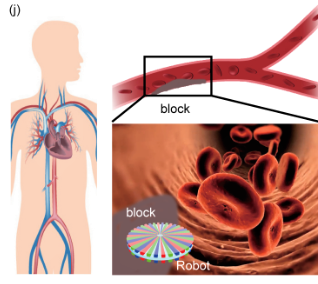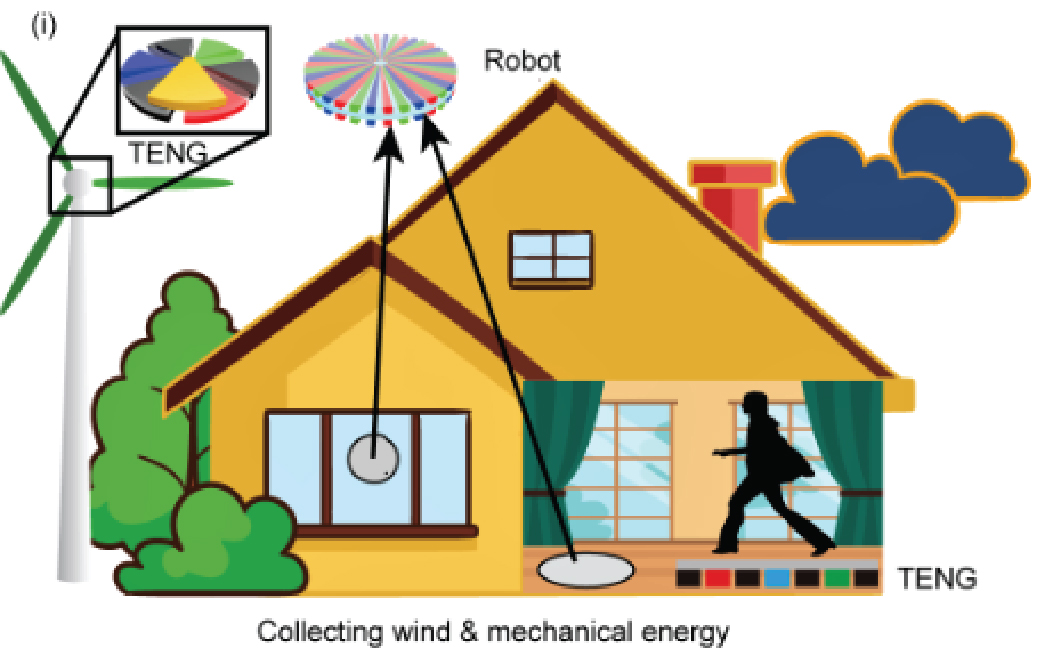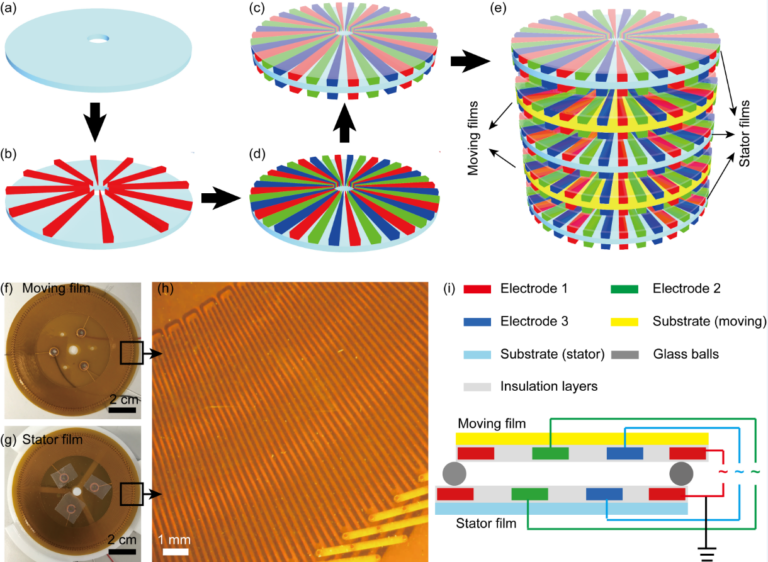
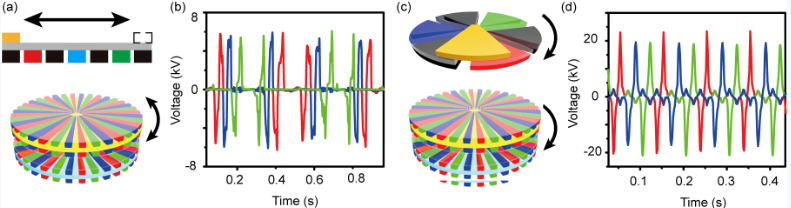
Flexible and ultra-thin robots can work in special environment, such as industrial use, cleaning systems and medical operations. However, powering micro robot systems is still a challenge. We develop a three-phased triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) that can convert mechanical energy in the environment into electrical energy, and hence produce a self-powered electrostatic robot. Potential applications include cleaning robot for home, thrombolytic therapy for severe blood clots, etc.
Uniqueness and Competitive Advantages:
- Flexible and ultra-thin system
- Three-phased TENG can convert mechanical energy in the environment into electrical energy
- Self-powered system does not require an external power supply
- Energy can be remotely transmitted and the movement of the robot can be precisely controlled