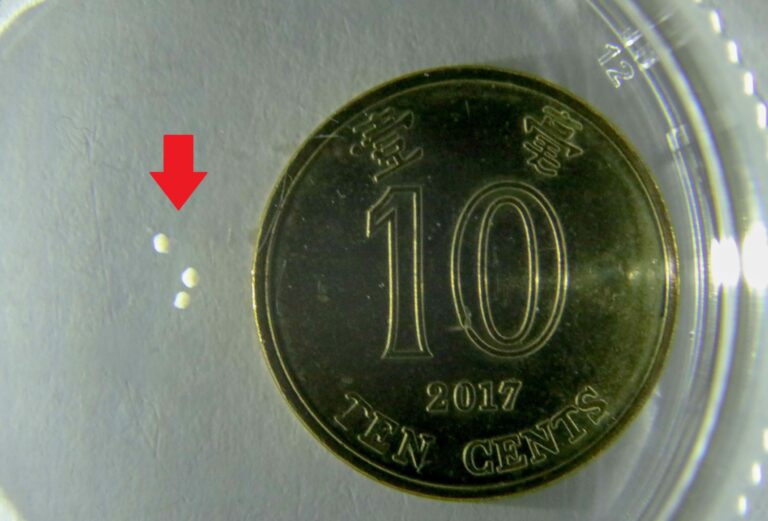
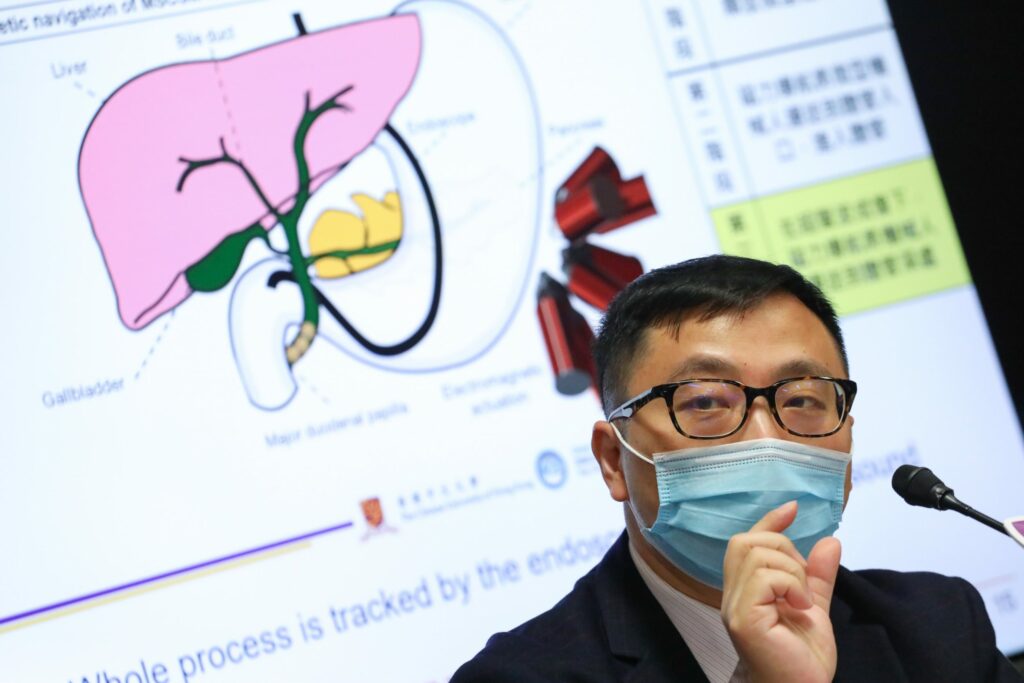
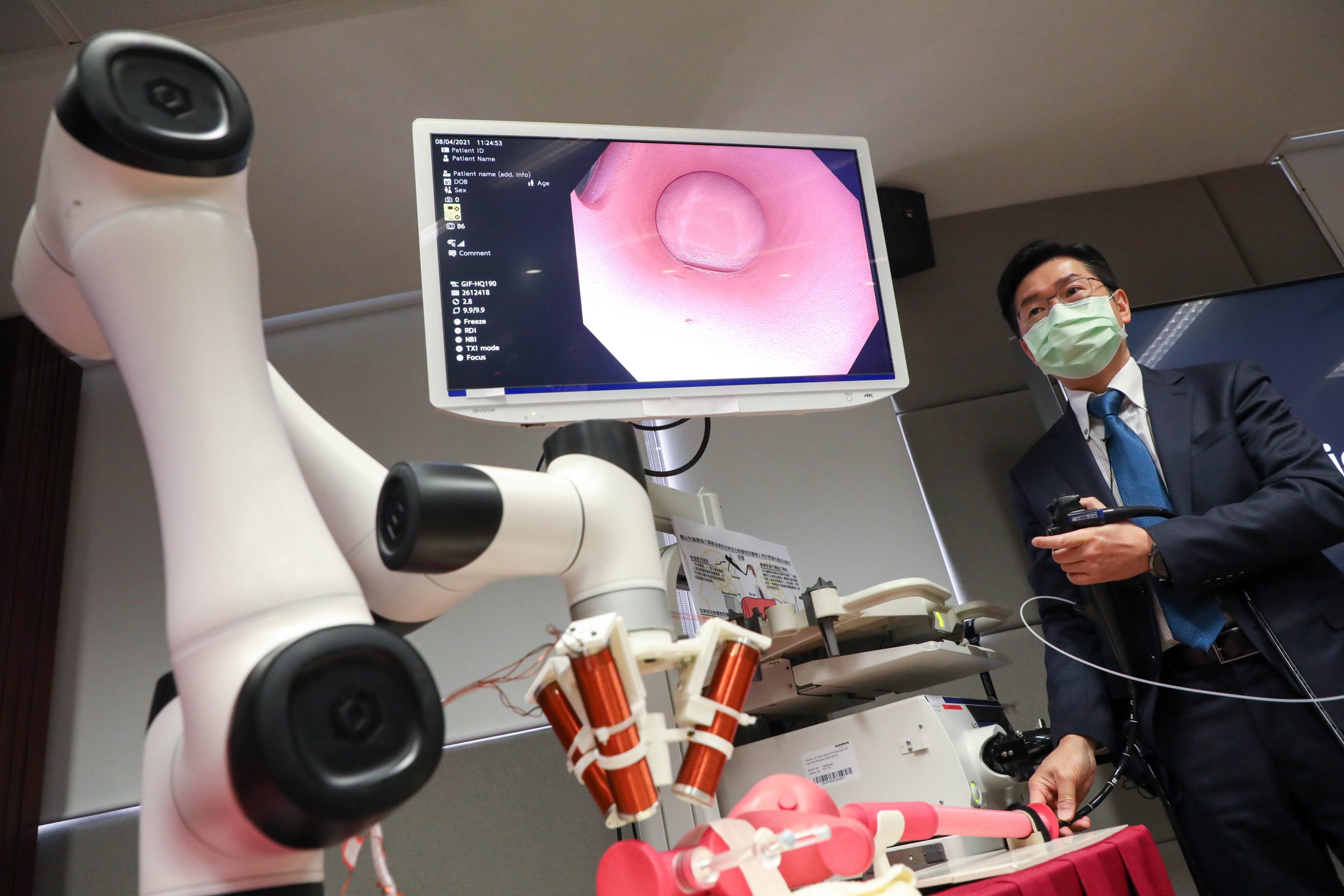
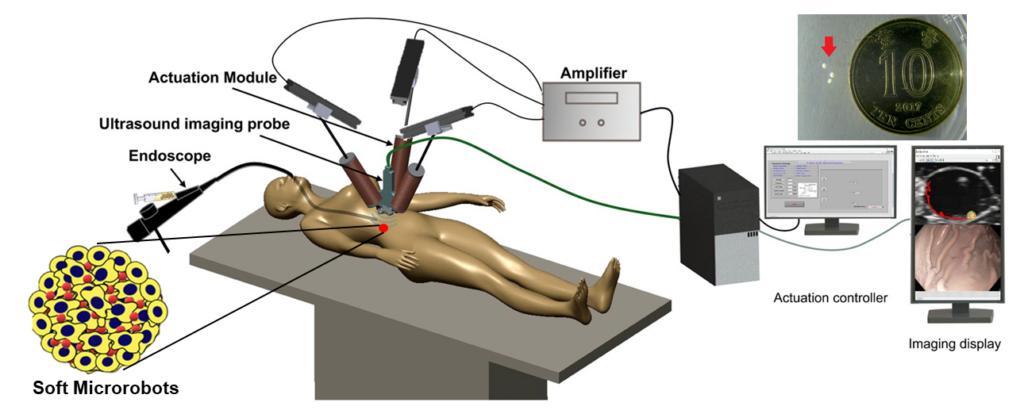
The soft microrobots are mainly composed of stem cells (~98%) and a tiny portion of magnetic particles (~2%), possessing an elastic modulus close to the human brain tissue. The stem cells can be harvested from the host to minimize immune responses during the in vivo delivery. The project has also developed endoscopy-assisted magnetic actuation with a dual imaging system (EMADIS). Endoscope offers “express lane” for soft microrobots to avoid the direct contact with complex physiological environment.
The microrobots not only have rapid response and precise targeting capability under the magnetic field, but also show excellent adaptability to the complex surroundings by self-alternating the shape during navigation inside the body.
The technology has the potential for treating various diseases in tiny and tortuous lumens which are hard-to-reach or inaccessible by regular medical devices.

Uniqueness and Competitive Advantages:
- First to integrate soft microrobots, endoscopy, magnetic navigation and ultrasound imaging for endoluminal delivery
- Greatly extends the reach and functionalities of endoscopy
- “Express lane” for soft microrobots to avoid the direct contact with complex physiological environment and bio-barriersRapid deployment of soft microrobot in tiny & tortuous lumens (~ 1 m in minutes)